ECE 5th SEM IMP QUESTIONS
QUESTIONS DetailsCONTROL SYSTEMS

1) Define transfer function.
2) What are the basic elements used for modeling
mechanical rotational system?
3) Name two types of electrical analogous for mechanical
system.
4) What is block diagram?
5) What is the basis for framing the rules of block
diagram reduction technique?
6) What is a signal flow graph?
7) Write
Definitions /Short Notes on:
- System
- Control System
Reference Input
- Output
- Feedback element
8) Classify
Control system.
10) Explain
importance of Feedback system.
11) Write
the rules of Block Diagram Reduction.
12) Explain
Mason’s Gain Formula.
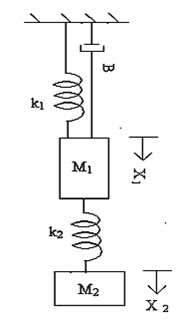
13) Write the
differential equations governing the Mechanical system shown in fig.
and
determine the transfer function.
14) Determine the
transfer function Y2(S)/F(S) of the system shown in fig.
15) Find the overall
gain of the system whose signal flow graph is shown in fig.
 16) Draw a signal flow graph and evaluate
the closed loop transfer function of a system
Whose block is shown in fig?
16) Draw a signal flow graph and evaluate
the closed loop transfer function of a system
Whose block is shown in fig?
 17) Derive the expressions and draw the
response of first order system for unit step input.
18) Draw the response of second order
system for critically damped case and when input is unit step.
19) Derive the
expressions for Rise time, Peak time, and Peak overshoot.
A
potential control system with velocity feedback is shown in fig. What is the
response
of the system for unit step input?
17) Derive the expressions and draw the
response of first order system for unit step input.
18) Draw the response of second order
system for critically damped case and when input is unit step.
19) Derive the
expressions for Rise time, Peak time, and Peak overshoot.
A
potential control system with velocity feedback is shown in fig. What is the
response
of the system for unit step input?
 20) For a unity feedback control system the
open loop transfer function
G(S) =
10(S+2)/ S2 (S+1). Find
(a)
Position, velocity and acceleration error constants.
(b) The steady state error when the input is R(S)
where R(S) =3/s –2/s2+1/3s3
21) What is frequency response?
22) What are advantages of frequency response
analysis?
23) What are frequency domain specifications?
24) Define Resonant Peak.
25) What is resonant frequency?
26) Define Bandwidth.
27) What is cut-off rate?
28) Define gain margin.
29) Define phase margin.
30) What is phase and Gain cross-over frequency?
31) What is Bode plot?
32) Define corner frequency.
33) What are the
advantages of Bode Plot?
34) Sketch the Bode plot and hence find Gain cross
over frequency, Phase cross over frequency, Gain margin and Phase margin.
G(S) = 0.75(1+0.2S)/ S (1+0.5S) (1+0.1S)
35) Sketch the polar plot for the following
transfer function and find Gain cross over frequency, Phase cross over
frequency, Gain margin and Phase margin.
G(S) = 400/ S (S+2) (S+10)
36) What is the necessary and sufficient condition
for stability?
37) What is routh stability condition?
38) What is Nyquist stability criterion?
39) Using Routh criterion determine the stability
of the system whose characteristics
equation
is s4+8s3+18s2+16s+5 =0 .
40) Construct Nyquist plot for a feedback control
system whose open loop transfer function is given by G(S)H(S) =5/ S(1-S).comment
on the stability of open loop and
closed
loop transfer function.
41) Sketch the Nyquist plot for a system with the
open loop transfer function
G(S)H(S) =K(1+0.5S) (1+S) / (1+10S) (S-1).determine the range of values
of K for which the system is stable.
42) What are state variables?
43) What is
the state space?
44) What are phase variables?
45) What is a state vector?
46) Test the controllability & observability of
the system whose state space representation is given as,
20) For a unity feedback control system the
open loop transfer function
G(S) =
10(S+2)/ S2 (S+1). Find
(a)
Position, velocity and acceleration error constants.
(b) The steady state error when the input is R(S)
where R(S) =3/s –2/s2+1/3s3
21) What is frequency response?
22) What are advantages of frequency response
analysis?
23) What are frequency domain specifications?
24) Define Resonant Peak.
25) What is resonant frequency?
26) Define Bandwidth.
27) What is cut-off rate?
28) Define gain margin.
29) Define phase margin.
30) What is phase and Gain cross-over frequency?
31) What is Bode plot?
32) Define corner frequency.
33) What are the
advantages of Bode Plot?
34) Sketch the Bode plot and hence find Gain cross
over frequency, Phase cross over frequency, Gain margin and Phase margin.
G(S) = 0.75(1+0.2S)/ S (1+0.5S) (1+0.1S)
35) Sketch the polar plot for the following
transfer function and find Gain cross over frequency, Phase cross over
frequency, Gain margin and Phase margin.
G(S) = 400/ S (S+2) (S+10)
36) What is the necessary and sufficient condition
for stability?
37) What is routh stability condition?
38) What is Nyquist stability criterion?
39) Using Routh criterion determine the stability
of the system whose characteristics
equation
is s4+8s3+18s2+16s+5 =0 .
40) Construct Nyquist plot for a feedback control
system whose open loop transfer function is given by G(S)H(S) =5/ S(1-S).comment
on the stability of open loop and
closed
loop transfer function.
41) Sketch the Nyquist plot for a system with the
open loop transfer function
G(S)H(S) =K(1+0.5S) (1+S) / (1+10S) (S-1).determine the range of values
of K for which the system is stable.
42) What are state variables?
43) What is
the state space?
44) What are phase variables?
45) What is a state vector?
46) Test the controllability & observability of
the system whose state space representation is given as,
 47) Determine the state variable representation of
the system whose transfer function is
given
as Y(s) / U(s) = 2s2+8s+7 / (s+2) 2 (s+1)
47) Determine the state variable representation of
the system whose transfer function is
given
as Y(s) / U(s) = 2s2+8s+7 / (s+2) 2 (s+1)




Read More | Comments
Read More | Comments
1.What is CMOS logic design? Why static power consumption is zero in CMOS logic design?
Read More | Comments
P O C
Q1.
(a) Explain antenna action. Define any of its four parameters.
(b) An antenna has an
effective height of 10m and the current at the base is 450A (rms) at 50 kHz.
Calculate the power radiated. If the total resistance of the antenna system is
1.5 ohm find out the efficiency of the antenna.
(c) How retarded
potentials are useful in deriving the radiated field due to any antenna?
(d) Show that the
directivity of an alternating current element is 1.76dB.
(e) Find the Gain, beam
width and capture area for a parabolic antenna with a 6 m diameter dish and
dipole fixed at a frequency of 10 GHz.
Q2. (a) Classify
various type of antenna array with example.
(b) Derive and draw the
radiation pattern of two isotropic sources separated by a distance with an initial phase of 90 degree.
(c) With the help of
pattern multiplication draw the radiation pattern of 4 element isotropic array
separated by with the initial phase of 0 degree among them.
(d) Design Yagi-Uda
antenna of 6 elements of provide gain of 10 dB if the operating frequency is
200 MHz
(e) Derive the
radiation resistance of a antenna.
(f) Derive the field
component of short electric dipole.
Q3. (a) Design a
helical antenna operating in the axial mode that gives a directivity of 14 dB
at 2.4 GHz. For this antenna, calculate the input impedance, half power
beamwidth, BWFN, and the axial ratio.
(b) Determine the
directivity of a loop antenna whose radius is 0.5m, when it is operated at
0.9MHz. Explain two of its applications.
(c) Design a log
periodic dipole array having a τ = 0.895 and σ =0.166 over a frequency range of
10 MHz to 30 MHz
Q4. (a) Why we use term
modified refractive index in propagation of radio waves. In which type of
propagation it is valid and what is its value?
(b) Explain the
structure of ionosphere. Explain any two parameters of sky wave propagation.
(c) What is
troposphere? Explain the mechanism of wave propagation in this region.Read More | Comments
Integrated Circuits
1.What is CMOS logic design? Why static power consumption is zero in CMOS logic design?
2.Realize the Half adder circuit using CMOS logic design.
3.Realize the full adder circuit using CMOS logic design.
4.Realize the function Z= A(B+C) using CMOS logic design.
5.Realize the function Z= A(B+CD)+B using CMOS logic design.
6.Design a NOR based SR latch in CMOS.
7.Design a NAND based SR latch using NMOS depletion load.
8.Design a NOR based D-FF in CMOS.
9.Realize AND, OR, NAND, NOR and NOT gate using CMOS logic design.
10.Realize the function Z= A+B(C+D) using CMOS logic design.
11.Draw the circuit diagram of 555 Timer and explain about it.
12.Design the Monostable multivibrator using 555 timer circuit and explain about it. Also derive the relevant expressions.
13.Design the Astable multivibrator using 555 timer circuit and explain about it. Also derive the relevant expressions.
14.Draw the block diagram of PLL and explain about it.
15.Draw the block diagram frequency divider circuit using PLL and explain about it.
16.Draw the block diagram amplitude modulator circuit using PLL and explain about it.
17.Draw and explain about the voltage controlled oscillator circuit.
18.How an Ex-OR gate can be used as a phase detector circuit.
Assignment Part 2
1. Draw and explain working of
negative peak detector with the help of suitable diagram and waveform.
2. Draw and explain working of
log amplifier.
3. With the help of multiplier IC
realize the operation of multiplication and division.
4. How Schmitt trigger is
removing errors of zero crossing detector? What are its advantages?
5. What do you mean by
multivibrator circuit? What are different types of MV?
6. Analyze the performance of one
shot MV. Derive the expression for time period.
7. Explain the function of
Gyrator circuit.
Read More | Comments
EME
Q1.
Explain the Meaning, nature and scope of Economics. Briefly explain the
two major branches of Economics
Q2 Write down a 5 point of difference
between macroeconomics and microeconomics.
Q3 Define engineering, science and
Technology? How does the three contribute to the economic development of a
country.
Q4 “Managerial economics is economics
applied in decision-making.” Explain.
Q5.What is managerial economics? How
does it differ from traditional economics?
Q6. Critically evaluate the impact of
technology on the economic development of a country.
Q7. Explain the various functions and
responsibilities of managerial economist
Q8
Write Short Notes on:-
a)
Engineering & Science
b)
Sloping downward of Demand Curve
c)
Various steps in demand forecasting.
d)
The concept of Elasticity of Demand
e)
External Economies
Q9.
What do you mean by Returns to a scale? What are the applications of
this law?
Q10. What do you mean by market? Briefly
explain the various types of Market Structures.
Q11.
Explain the following concept:-
(i) Price Elasticity of demand
(ii) Income Elasticity of demand
Q12.
Explain determinants of Demand. What is demand forecasting? What is its purpose
& significance in business organization?
Q13
State the Law of variable proportion. What are the applications of this law?
Q14. Economic
Development of any country is closely associated with Science, Engg &
technology. Elaborate this statement and elucidate the role of science, engg
& technology in the economic development.
Q15 What useful information do these
concepts of elasticity provide to the
management?
Q16 Explain Internal Economies of Scale.
Q17 i) Fixed Cost
ii. Variable Cost
iii. Average Cost
iv .Marginal Cost
Q18 Define Monopolistic Competitive
market. What type of demand curve does a firm have under Monopolistic Competitive
Market?
Q19 Define Perfectly Competitive Market.
What type of Demand Curve does a firm
have under perfect competition?
Assignment
Questions
Q1 What useful information do these
concepts of elasticity provide to the
management?
Q2 Explain Internal Economies of Scale.
Q3 i) Fixed Cost
ii. Variable Cost
iii. Average Cost
iv .Marginal Cost
Q4 Define Monopolistic Competitive
market. What type of demand curve does a firm have under Monopolistic Competitive
Market?
Q5
Define Perfectly Competitive Market. What type of Demand Curve does a firm have under perfect competition?
Read More | Comments
MICROPROCESSOR
Q1.
Write a program to turn on and turn off the light for every 2 seconds. Use data
bit D4 to operate the light. Also show the delay calaculation and assume system
frequency 5Mhz.
Q2.
Write a program to generate the square wave with a 200µs on period and 400µs
off period. Also show the delay calaculation and assume system frequency 2Mhz.
Q3.
Write a program to:
a) Clear
the accumulator.
b) Add
45H
c) Subtract
90H
d) Add
64H
e) Display
the results after subtracting and after adding 64H.
Specify
the answers you would expect at the output ports.
Q4.Write
a program to load the bit pattern 91H in register B and 87H in register C. Mask
all the bits except D0 from the registers
B and C. If D0 is at logic1 in both registers, turn on the light
connected to the D0 position of output port 01H; otherwise, turn off the light.
Q5.
A set of eight data bytes is stored in memory location starting at XX50 H.
Write a program to check each data byte for the bits D7 and D0. If D7 or D0 is
0, reject the data byte; otherwise, store the data bytes at memory locations
starting at XX60hH.
Data(H)
: 80,52,E8,78,67,35,62, F5
Q6.
A set of eight data bytes is stored in memory location starting at XX50 H.
Write a program to check whether a byte 40H exist in the set. If it does, stop
checking and display its memory location; otherwise output FF H.
Data
(H) : 48,32,F2,38,37,40,82,8A
Q7.
Six bytes of data are stored in memory locations starting at XX60H. Write a
program to add all data bytes. Use register c to save any carries generated,
while adding the data bytes. Display the entire sum at two output ports.
Data
(H): A2,54,A2,86,5B,25
Q8.
Draw the flowchart to load the hexadecimal numbers 90 H and A5 H in registers D
and E respectively and add the numbers. If the sum is greater than FFH, display
01H at port 0; otherwise, display the sum.
Q9.
Write a program to provide the given on/off time to three traffic lights
(Green, Yellow and Red) and two pedstrain signs(WALK and DON’T WALK). The
signal lights and signs are turned on/off by the data bits of an output port as
shown below:
Lights
|
Data Bits
|
On Time
|
1.
Green
|
D7
|
20 seconds
|
2.
Yellow
|
D6
|
10 seconds
|
3.
Red
|
D4
|
20 seconds
|
4.
WALK
|
D2
|
20 seconds
|
5.
DON’T WALK
|
D0
|
30 seconds
|
The
traffic and pedestrain flow are in the same direction; the pedstrain should
cross the road when the Green light is on.
Q10.
Write a program to control a railway crossing signal that has two alternately
flashing red lights, with a 1 second delay on time for each light.
Q11.
Write a 20ms time delay subroutine using register pair BC. Clear the Z flag
without affecting any other flags in the flag register and return to the main
program.
Q12.
Write a program to add the two hex numbers 7A and 46 and to store the sum at
memory location XX98H and the flag status at location XX97H.
Q13.
An 8bit binary no. is stored in memory
location XX50H. Write a program to transfer the byte to the accumulator
and Separate the two nibbles.
Also call the subroutine to convert each nibble into
ASCII hex code and
Store the codes in memory location XX60H and XX61H.
Q14. A BCD no. between 0 and 99 is stored in an R/W
memory location called the input buffer (INBUF). Write a main program and a
conversion subroutine (BCDBIN) to convert the BCD no. into its binary equivalent.
Store
the result in a memory location defined as the output buffer (OUTBUF).
Q15. A set of six unpacked BCD no. is stored
in memory locations starting at XX30 H. Assume the seven segment codes of the
digits 0 to 9 for common cathode LED are stored in memory
location starting at XX70 H. Write a program to select an appropriate seven
segment code for each digit. The code should be stored in memory location in
reverse order starting at XX90 H.
Q16.Calculate the delay in
the following loop, assuming the system clock period is 0.5microseconds:
LXI B, 12FF
H 10
DELAY: DCX B 6
XTHL 16
NOP 4
MOV A,
C 4
ORA B 4
JNZ
DELAY 10/7
Q17. A set of ten packed BCD no. is stored in
memory location starting at XX40 H.
i) Write a program to add these numbers in
BCD. If a carry is generated save it in register B and adjust it for BCD. The
final sum will be less than 9999BCD .
ii) Write a second subroutine to unpack the
BCD sum stored in register A and B and Store them in the memory location
starting at XX60 H. (MSB at XX60 H and LSB at XX63 H)
Q18. With reference to Q17. Write a
subroutine to convert the unpacked BCD digits stored at XX60 to XX63 H into
ASCII code and store them at output buffer memory starting at XX80 H.
Q19.
Write a program to subtract two packed BCD numbers (75- 36) stored in register B
and C respectively. The minuend is placed in register C and subtrahend is
placed in register B. Display the result at output port 0.
Q20.
A binary number is stored in memory location XX50 H. Convert the no. into BCD
and store each BCD as two unpack BCD digits in the output buffer (XX70 H). to
perform the task, write a main program and two subroutines: one to supply
powers of 10 and the other to perform the conversion.
Read More | Comments